Kerala Declares Bacillus Subtilis ‘State Microbe’
Syllabus: GS2/ Health/ Governance
Context
- Kerala has become the first Indian state to designate an official “State Microbe,” selecting Bacillus subtilis, a beneficial, soil-dwelling bacterium.
About Bacillus subtilis
- It is a non-pathogenic, rod-shaped, gram-positive bacterium found commonly in soil, water, and the human gut.
- Bacillus subtilis is a probiotic or good bacterium that plays a vital role in improving gut health and strengthening immunity.
- The bacterium is widely used in agriculture as a biofertilizer and biocontrol agent to enhance crop productivity and suppress plant diseases.
- Due to its resilience and spore-forming ability, it has significant industrial and biotechnological applications.
Centre of Excellence in Microbiome
- The Centre of Excellence in Microbiome (CoEM), established by the Government of Kerala under the Kerala State Council for Science, Technology and Environment.
- Located in Thiruvananthapuram, is India’s first dedicated multi-domain research institution for microbiome studies.
Source: TH
Quadrilateral Security Dialogue (Quad)
Syllabus: GS2/ International Relations
Context
- Recent remarks from senior U.S. officials describing the Quadrilateral Security Dialogue (Quad) as a “very important platform” and India as an “active participant” underline the grouping’s centrality to India’s Indo-Pacific strategy.
Quadrilateral Security Dialogue (QUAD)
- It is an informal multilateral grouping of India, the U.S., Australia, and Japan aimed at cooperation for a free and open Indo-Pacific region.
- Origin: The Quad began as a loose partnership after the 2004 Indian Ocean tsunami when the four countries joined together to provide humanitarian and disaster assistance to the affected region.
- It was formalized by former Japanese Prime Minister Shinzo Abe in 2007, but then fell dormant.
- After a decade it was resurrected in 2017, reflecting changing attitudes in the region toward China’s growing influence.
Strategic Significance for India
- Maritime Security and Indo-Pacific: The Quad strengthens coordination in safeguarding Sea Lines of Communication (SLOCs).
- It complements India’s SAGAR (Security and Growth for All in the Region) vision.
- Balancing Regional Power Asymmetry: The Quad is viewed as a response to growing assertiveness by China in the South China Sea and the broader Indo-Pacific.
- However, India maintains that the Quad is not a military alliance but a platform for cooperative security.
Source: TH
African Union
Syllabus: GS2/Regional Groupings
Context
- The African Union is hosting its annual summit in Ethiopia to discuss the future of the continent, as the organization faces widespread discontent.
African Union
- The African Union (AU) is a continental body consisting of the 55 member states that make up the countries of the African Continent.
- It was officially launched in 2002 as a successor to the Organisation of African Unity (OAU, 1963-1999).
- Aim: To realise Africa’s potential and to focus towards increased cooperation and integration of African states to drive Africa’s growth and economic development.
- Headquarters: Addis Ababa, Ethiopia.
- Initiatives of the AU include the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) agreement, aiming to create a single market for goods and services across the continent, and Agenda 2063, a strategic framework for the socio-economic transformation of the continent over the next 50 years.
Source: IE
Seva Teerth
Syllabus: GS2/Governance
In News
- The Prime Minister inaugurated the Seva Teerth complex in New Delhi, along with Kartavya Bhavan-1 and 2.
Seva Teerth and Kartavya Bhavan-1 and 2
- Seva Teerth houses the Prime Minister’s Office, the National Security Council Secretariat, the Cabinet Secretariat, all of which were previously located across different locations.
- It consolidates administrative functions within modern, and future-ready facilities.
- Kartavya Bhavan-1 and 2 accommodate several Key ministries including the Ministry of Finance, Ministry of Defence, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Ministry of Education and the Ministry of Information and Broadcasting.
- Both building complexes feature digitally integrated offices, structured public interface zones and centralised reception facilities.
Importance
- These features will foster collaboration, efficiency, seamless governance, improved citizen engagement and enhanced employee well-being.
Source :Air
CPI January, 2026 (Provisional) at Base year 2024=100 Released
Syllabus:GS3/Economy
Context
- The Ministry of Statistics & Programme Implementation has released the provisional Consumer Price Index (CPI) with Base 2024=100.
About
- The base has been revised from 2012 to 2024 using Household Consumption Expenditure Survey 2023-24.
- 12 Divisions in place of 6 Groups in accordance with Classification of Individual Consumption According to Purpose (COICOP) 2018.
- COICOP is the international classification of household expenditure developed by the United Nations Statistics Division.
- The objective of the COICOP is to provide a framework of homogeneous categories of goods and services from the point of view of its usage by the households.
- Its adoption ensures that India’s CPI is comparable with CPIs worldwide.
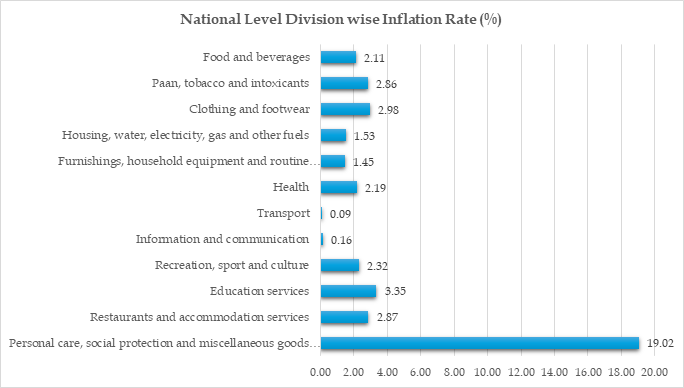
Consumer Price Index (CPI):
- CPI measures the average change in prices paid by consumers for a basket of goods and services over time i.e., it tracks retail inflation.
- Tracks cost of living and purchasing power.
- Includes items like food, housing, clothing, transport, etc.
- It is published monthly, the earlier base year: 2012 which is revised to 2024.
- Released By: NSO, MoSPI.
Revision of Base Year
- It has been introduced to ensure that the index remains representative of current household consumption patterns, price structures, and the evolving nature of the Indian economy.
- The Base Year is a chosen year taken as a reference point (index = 100) to compare prices over time.
- It is important because it helps measure how much prices have increased or decreased and keeps inflation figures relevant.
- The base updation exercise mainly involves revising the CPI item basket and updating item weights based on the latest Household Consumption Expenditure Survey (HCES).
Source: PIB
Mangrove Clam
Syllabus: GS3/Environment
In News
- The ICAR–Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute (CMFRI)ICAR–Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute (CMFRI) has successfully achieved induced breeding of the mangrove clam (Geloina erosa) under captive conditions.
Mangrove clams
- It is commonly known as mud clams and it is ecologically important.
- It typically inhabits organic-rich muddy substrates in intertidal mangrove zones.
- It is a dwindling bivalve species distributed across mangrove and estuarine ecosystems in South and Southeast Asia.
- It continues to be a valued local delicacy in several parts of India, particularly in northern Kerala, where the species is popularly known as “Kandal Kakka”.
Source : DD
Revised Guidelines For the Lead Bank Scheme (LBS)
Syllabus: GS3/Economy
In News
- The RBI’s proposed guidelines aim to strengthen and streamline the Lead Bank Scheme by clearly defining the structure, membership, and roles of various committees
Lead Bank Scheme (LBS)
- The Lead Bank Scheme (LBS) originated from the 1969 Gadgil Study Group, which highlighted the inadequate rural presence and orientation of commercial banks and recommended an “Area Approach” for developing rural banking and credit structures.
- This was endorsed by the Nariman Committee, which proposed that each public sector bank act as a “Lead Bank” in specific districts to fulfill social responsibilities.
- Based on these recommendations, the RBI introduced the LBS in December 1969 to coordinate banks and development agencies at the district level.
- It aims to enhance credit flow to priority and rural sectors, and promote overall rural development through designated Lead Banks.
RBI’s Proposed Guidelines
- It reinforces the functioning of State Level Bankers’ Committees (SLBCs) and Lead District Manager offices.
- A designated commercial bank will act as the Lead Bank in each district to coordinate credit institutions, government bodies, and stakeholders to improve priority sector lending and financial inclusion.
- SLBC Convenor Banks will oversee banking activities at the state level and address operational lending issues with state governments.
- The scheme will operate through a three-tier structure—Block Level Banker’s Committee (BLBC) at block level, District Consultative Committee (DCC) and District Level Review Committee (DLRC) at district level, and SLBC/UTLBC at the state/UT level.
- Banks are also required to monitor and aim for a 60% Credit-Deposit ratio in rural and semi-urban branches nationwide.
Source: TH
Previous article
India’s AI Stack For Population-Scale Impact